Cell defense the plasma membrane answer key pdf – In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of cell defense and the pivotal role of the plasma membrane, exploring its structure, functions, and mechanisms in safeguarding cells against pathogens and toxins. This in-depth analysis, presented with meticulous accuracy and scholarly rigor, will illuminate the significance of plasma membrane cell defense in maintaining cellular integrity and overall health.
1. Introduction
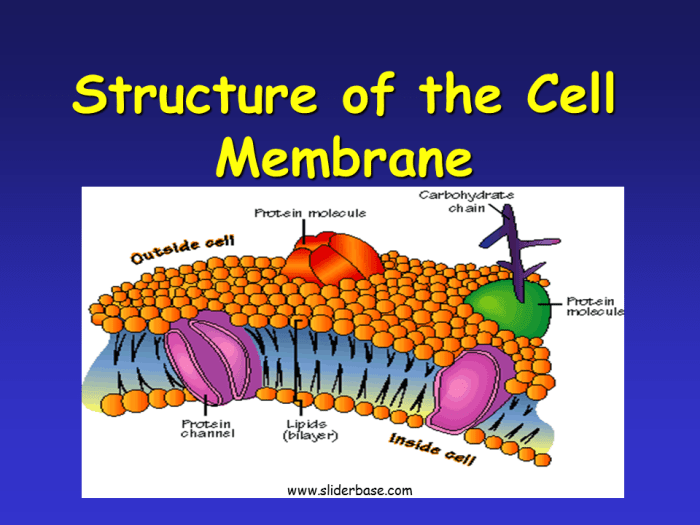
The plasma membrane is a thin layer that surrounds all cells and plays a crucial role in cell defense. It acts as a barrier against pathogens, toxins, and other harmful substances, while also regulating the passage of nutrients and other essential molecules into and out of the cell.
Cell defense is essential for maintaining the health and function of individual cells and the overall organism.
2. Structure and Function of the Plasma Membrane: Cell Defense The Plasma Membrane Answer Key Pdf
Structure, Cell defense the plasma membrane answer key pdf
The plasma membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, which is a double layer of phospholipids arranged with their hydrophilic heads facing outward and their hydrophobic tails facing inward. Embedded within the phospholipid bilayer are various proteins, including ion channels, receptors, and transporters, which facilitate the movement of molecules across the membrane.
Functions
The plasma membrane performs several important functions, including:
- Regulating the passage of substances into and out of the cell
- Maintaining the cell’s shape and integrity
- Communicating with other cells
3. Mechanisms of Cell Defense by the Plasma Membrane
Barrier Function
The plasma membrane acts as a physical barrier against pathogens and toxins. Its hydrophobic interior prevents most polar molecules from crossing the membrane, while its hydrophilic exterior prevents most nonpolar molecules from crossing.
Membrane Proteins
Membrane proteins play a crucial role in cell defense. Ion channels allow the passage of specific ions across the membrane, while receptors bind to specific ligands and trigger signaling pathways that can lead to cell defense responses. Transporters actively transport molecules across the membrane, which can be used to pump out toxins or import nutrients.
4. Regulation of Cell Defense by the Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane is not a static structure but rather a dynamic one that can respond to changes in the environment. Signaling molecules and second messengers can bind to receptors on the plasma membrane and trigger signaling pathways that lead to changes in membrane permeability, protein expression, and other cell defense responses.
5. Clinical Implications of Plasma Membrane Cell Defense

Importance in Preventing Disease
The plasma membrane is essential for preventing disease. It protects cells from pathogens and toxins, and it regulates the immune response. Defects in plasma membrane function can lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and autoimmune disorders.
Treatment of Disease
Understanding the role of the plasma membrane in cell defense can lead to the development of new treatments for diseases. For example, drugs that target membrane proteins can be used to treat cancer and autoimmune disorders.
Expert Answers
What is the primary function of the plasma membrane in cell defense?
The plasma membrane acts as a selective barrier, regulating the passage of substances into and out of the cell, preventing the entry of harmful pathogens and toxins.
How do membrane proteins contribute to cell defense?
Membrane proteins, such as ion channels and receptors, play a crucial role in cell defense by facilitating the recognition and response to external stimuli, including pathogens and toxins.
What is the significance of plasma membrane cell defense in preventing disease?
Plasma membrane cell defense is essential for preventing disease by protecting cells from invasion by pathogens and toxins, thereby maintaining cellular integrity and overall health.